unveiling-the-secrets-of-barracuda
Discover the Secrets of Barracuda Fish: Fast, Fierce, and Beautiful

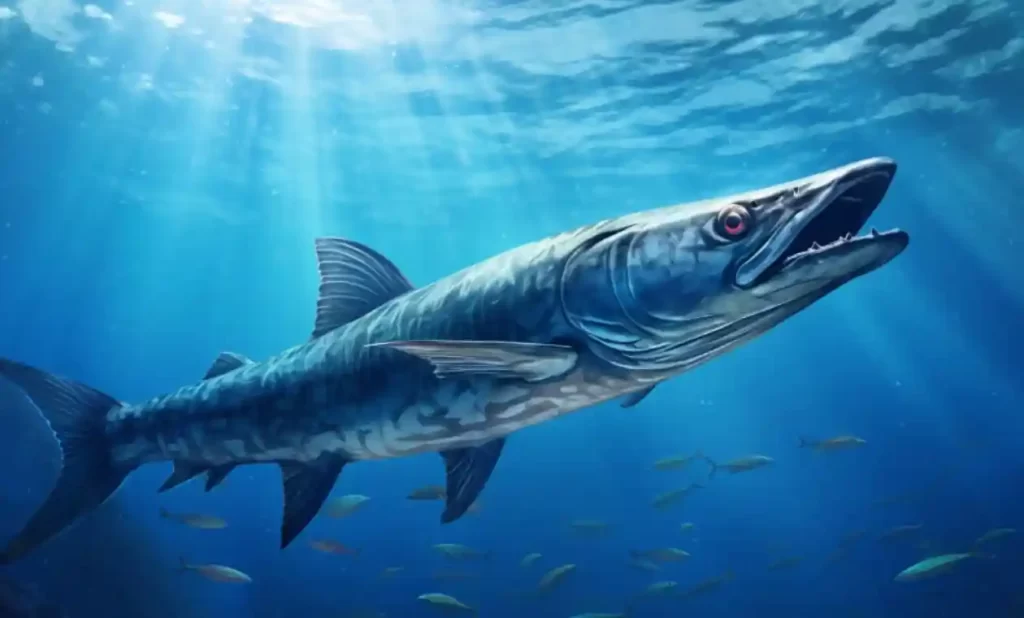
Once upon a time, in the big blue ocean, there lived a fascinating fish called the barracuda! Have you ever heard of a barracuda? They are special fish that are very important in the underwater world. Let’s dive in and learn more about these amazing creatures!
Scientific Name:
The scientific name of the barracuda is “Sphyraena.” This special name comes from ancient Greek words. “Sphyraena” means “pike-like” or “spear-like.” It describes the shape of the barracuda, which is long and thin, just like a spear. So, when scientists say “Sphyraena,” they are talking about the barracuda fish that looks like a sharp spear in the water!
Life Span:
Barracuda fish can live for a long time, just like how we grow older as we get bigger. On average, a barracuda fish can live up to 10 to 15 years. But do you know what can influence their lifespan? Several things can make a difference. If they have plenty of food to eat, a safe and clean environment to live in, and if they stay away from dangers like predators, they have a better chance of living longer. So, just like us, barracuda fish need to stay healthy and safe to have a long and happy life!
Top Speed:
Did you know that barracuda fish are incredibly fast swimmers? They can zip through the water like a rocket! A barracuda can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour (40 kilometers per hour). That’s even faster than some cars! Imagine swimming as fast as a barracuda—it would be so exciting! Their speed helps them catch their prey and escape from any bigger fish that might want to eat them. So, when it comes to swimming, the barracuda is definitely one of the speediest creatures in the ocean!
Weight:
Barracuda fish come in different sizes, just like we come in different heights and weights. On average, a barracuda fish can weigh anywhere between 10 to 100 pounds (4.5 to 45 kilograms). That’s like carrying a really heavy backpack! The weight of a barracuda can vary depending on its age, species, and the food it eats. Some barracudas can grow to be really big and weigh even more than 100 pounds! It’s amazing to think about how strong and powerful these fish can be!
Length:
Barracuda fish can grow to be quite long, just like a stretchy rope! On average, a barracuda can be about 3 to 6 feet long (1 to 2 meters). That’s like the height of a grown-up person! Some barracudas can even grow longer, reaching up to 10 feet (3 meters) in length. They have sleek bodies that help them swim quickly through the water.
Compared to other fish species, barracudas are considered to be on the larger side. They are longer than many other fish you might see in the ocean. However, there are some fish that can grow even longer than barracudas, like the magnificent marlin and the gigantic whale shark. It’s fascinating to learn about the different sizes and lengths of the underwater creatures, isn’t it?
Appearance:
Let’s take a close look at how a barracuda fish looks! Picture a fish with a sleek and slender body, just like a shiny torpedo in the water. Its body is long and cylindrical, which means it’s shaped like a tube.
The skin of a barracuda is covered in shiny scales that sparkle when they catch the sunlight. Some barracudas have a silvery or grayish color, while others can have hints of green or blue on their backs. They are truly eye-catching!
One of the most notable features of a barracuda is its mouth full of sharp teeth. When you see a barracuda’s mouth, you might feel like you’re looking at a fierce predator. Their teeth are long, pointy, and razor-sharp, just like tiny daggers! These teeth help them catch and hold onto their prey, making sure they don’t get away.
Overall, with their streamlined body and menacing teeth, barracudas are like underwater hunters, ready to chase and capture their next meal. They are truly remarkable creatures to behold!
Unique Physique:
The barracuda has some truly unique features that make it stand out in the underwater world. Let’s explore them!
Firstly, the barracuda has an elongated body shape. Imagine a long, slender fish that looks like it’s been stretched out. This shape helps the barracuda swim through the water with incredible speed and agility. It’s like they were born to be swift swimmers!
Another striking feature of the barracuda is its powerful jaws. Their jaws are designed to be strong and filled with rows of sharp teeth. These teeth are not only sharp but also razor-edged, making them perfect for tearing through the flesh of their prey. With their jaws and teeth, barracudas are expert hunters, always ready to catch their next meal.
To add to their unique physique, barracudas also have a large, prominent eye on each side of their head. These eyes are keen and alert, helping them spot their prey even from a distance. It’s like they have built-in binoculars!
When you put all these features together— the elongated body, powerful jaws, and sharp eyes—you can see why the barracuda is such a formidable predator in the underwater world. They are well-equipped for hunting and survival in their marine habitats!
Types of Barracuda:
There are different types of barracuda fish found in oceans around the world, each with its own special characteristics. Let’s discover a few of them!
1. Great Barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda):

The great barracuda is the largest type of barracuda fish, and it can grow up to an impressive length of 6 feet (2 meters). When you look at a great barracuda, you’ll notice its sleek body that shines with a silver or grayish color. Along its body, you’ll see dark bands that run horizontally, giving it a unique and striking appearance.
One remarkable thing about the great barracuda is its speed. It can swim incredibly fast, like a bolt of lightning in the water. With its streamlined body and strong muscles, it can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour (40 kilometers per hour). That’s faster than many other fish in the ocean!
But speed is not the only impressive feature of the great barracuda. It also has a set of powerful jaws that are filled with sharp, razor-like teeth. These teeth are perfect for capturing and tearing apart their prey. With their strong jaws and teeth, great barracudas are skilled hunters and can snatch their meals in a flash.
In terms of habitat, great barracudas prefer warm and tropical waters, such as those found in the Caribbean Sea and the western Atlantic Ocean. They often inhabit coral reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds, where they can hide and wait for their next meal to come by.
Great barracudas are known to be solitary creatures, which means they usually swim alone rather than in groups. They are also quite territorial, defending their preferred hunting areas from other barracudas or intruders.
It’s important to remember that while great barracudas are powerful and fascinating, they are wild animals and should be observed from a safe distance if encountered during snorkeling or diving adventures.
With their impressive size, silver-gray coloration, incredible speed, and powerful jaws, the great barracuda truly commands attention in the underwater world. They are a captivating sight to behold!
2. Pickhandle Barracuda (Sphyraena jello):

The pickhandle barracuda is a fascinating type of barracuda fish with its own unique characteristics. While smaller in size compared to the great barracuda, it still grows to an average length of around 3 feet (1 meter).
One of the standout features of the pickhandle barracuda is its distinct coloration. Its body has a yellowish hue that gives it a vibrant appearance in the water. Along the sides of its body, you’ll notice dark spots or stripes that add to its striking pattern. These markings can vary in intensity and arrangement, making each pickhandle barracuda look slightly different from the others.
When it comes to speed, pickhandle barracudas are no slouches. While not as fast as the great barracuda, they are still agile swimmers, darting through the water with impressive speed to catch their prey. They rely on their streamlined body and strong muscles to move swiftly and efficiently.
In terms of habitat, pickhandle barracudas are commonly found in tropical and subtropical waters, particularly in the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. They tend to inhabit areas with coral reefs, rocky formations, and seagrass beds. These habitats provide them with places to hide and offer a diverse range of prey.
Pickhandle barracudas are known to be opportunistic feeders, meaning they eat a variety of small fish and other marine creatures that they come across. They are skilled hunters and use their sharp teeth to grasp and swallow their prey whole.
While pickhandle barracudas may not grow as large as their great barracuda counterparts, their vibrant yellowish color, distinctive markings, and agile swimming abilities make them a captivating sight in the underwater world. They showcase the diversity and beauty of barracuda species.
3. Guinean Barracuda (Sphyraena afra):
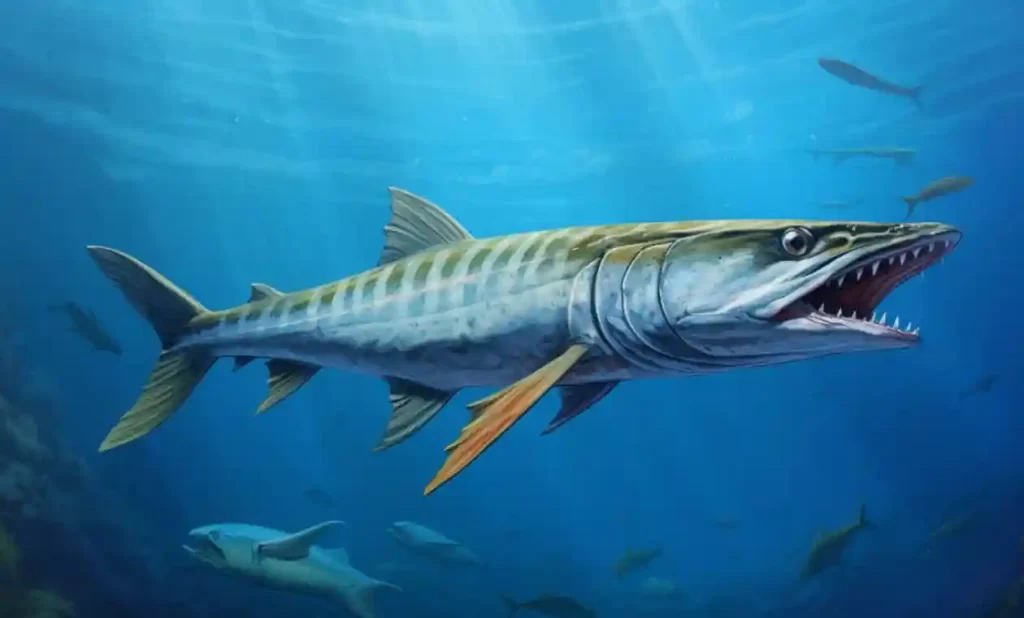

The Guinean barracuda is a fascinating species of barracuda fish that can be found in the waters off the West African coast. With their silver-gray body, they blend in with the surrounding ocean environment. They can grow up to an impressive length of 4 feet (1.2 meters), making them a formidable presence in the underwater world.
One notable characteristic of Guinean barracudas is their sharp teeth. Like other barracuda species, they possess a set of razor-sharp teeth that are designed for capturing and devouring their prey. These teeth enable them to be efficient predators, ensuring their success in hunting for food.
Guinean barracudas are known for their fierce predatory nature. They are skilled hunters that rely on their speed, agility, and keen senses to locate and pursue their prey. With their powerful muscular bodies and streamlined shape, they are capable of swift bursts of movement to catch smaller fish and other marine creatures.
These barracudas prefer to inhabit tropical waters along the West African coast, where they can find suitable feeding grounds. They are often found in coral reefs, rocky areas, and near underwater structures that provide hiding places and ambush points.
As voracious feeders, Guinean barracudas have a diverse diet that includes various small fish and other marine organisms. They strike swiftly and use their sharp teeth to seize and consume their prey.
Observing Guinean barracudas in their natural habitat is an awe-inspiring sight. Their silver-gray coloration, sharp teeth, and predatory behavior showcase their adaptation to life as efficient hunters in the vibrant ecosystems of West African waters.
4. Blackfin Barracuda (Sphyraena qenie):
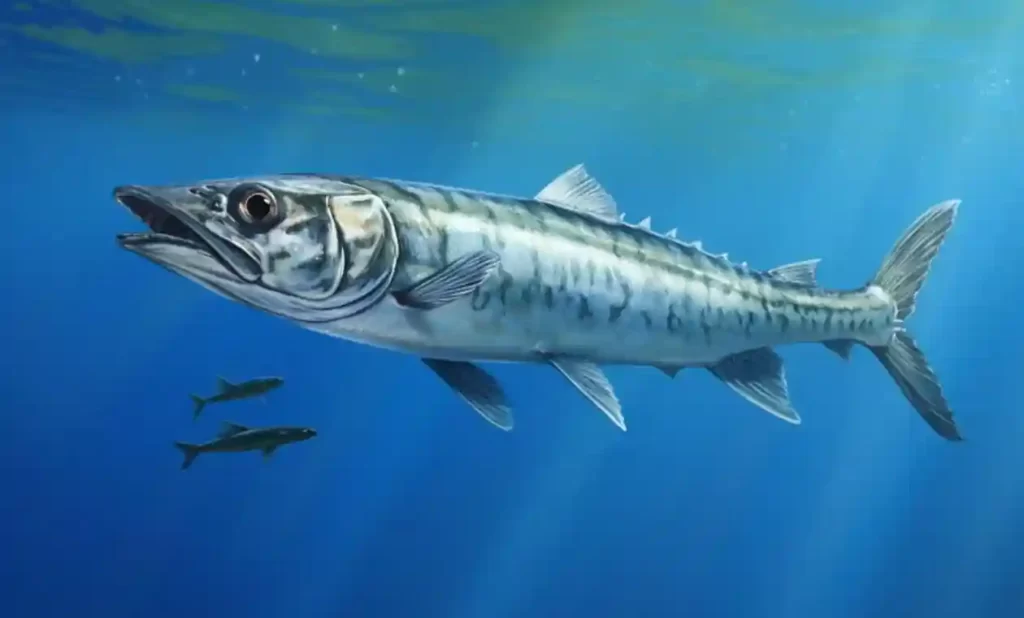
The Blackfin barracuda, as the name suggests, is characterized by its distinctive black fins and silver body. This species of barracuda is commonly found in the tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
The Blackfin barracuda has a sleek and slender body, typical of barracuda fish. Its silver-colored body allows it to blend in with its surroundings, making it a stealthy predator in the ocean. The standout feature of this barracuda is its striking black fins, which create a beautiful contrast against its silver body.
When it comes to speed, the Blackfin barracuda is known for its agility. It can swim swiftly through the water, using its streamlined body to propel itself. While specific speed measurements may vary, barracudas in general are renowned for their ability to reach impressive speeds.
In terms of habitat, Blackfin barracudas prefer the warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. They are commonly found near coral reefs, rocky areas, and underwater structures that provide shelter and hunting opportunities.
Blackfin barracudas are skilled hunters and feed on a variety of prey, including small fish and other marine organisms. They employ their sharp teeth and quick reflexes to capture and consume their meals.
These barracudas are generally known to be solitary creatures, preferring to swim alone rather than in groups. This behavior allows them to efficiently hunt and protect their territory.
The Blackfin barracuda, with its silver body and striking black fins, is a remarkable sight in the ocean. Its agility, predatory nature, and adaptability to various marine environments make it a fascinating species to observe and study.
These are just a few examples of the various types of barracuda fish that exist. Each type has its own unique coloration, size, and habitat preferences, but they all share the common traits of being fast and skilled hunters.
It’s fascinating to think about the different kinds of barracudas swimming in our oceans, each with its own special characteristics that make them truly remarkable!
Habits and Lifestyle:
Barracuda fish have interesting habits and a unique lifestyle that contribute to their success as predators in the underwater world. Let’s delve into their habits and lifestyle!
Barracudas are primarily found in warm waters, such as those in tropical and subtropical regions. They thrive in environments like the Caribbean Sea, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Indo-Pacific region. These warm waters provide the ideal conditions for their survival and contribute to their vibrant and diverse habitats.
One prominent aspect of a barracuda’s lifestyle is its hunting behavior. Barracudas are fierce and opportunistic predators. They are known for their ambush tactics and lightning-fast attacks on unsuspecting prey. They have a keen eye for spotting movement and can swiftly accelerate to capture their target. Their streamlined body and strong muscles enable them to swim swiftly and with great precision.
Barracudas are not picky eaters. They have a varied diet that includes small fish, crustaceans, and even squid. They rely on their sharp teeth and powerful jaws to seize and consume their prey. Their hunting techniques often involve stalking their victims, using their speed to their advantage, and striking with a sudden burst of energy.
In terms of social behavior, barracudas are typically solitary creatures. They tend to swim alone rather than in groups. This solitary nature allows them to focus on their hunting activities and maintain their territory without competition from other barracudas.
Barracudas are highly adaptable and can inhabit a range of marine environments, including coral reefs, rocky areas, seagrass beds, and open waters. They utilize these habitats for shelter, camouflage, and hunting opportunities.
It’s important to note that while barracudas are formidable predators in their natural habitats, they generally do not pose a threat to humans. They are not typically aggressive towards humans unless provoked or cornered. However, it is always recommended to maintain a respectful distance and avoid any unnecessary interaction with wild barracudas.
Understanding the habits and lifestyle of barracuda fish gives us insight into their remarkable adaptation to their environments. Their preference for warm waters, hunting behaviors, and solitary nature contribute to their success as skilled predators in the underwater realm.
Diet and Nutrition:
Barracudas are carnivorous predators, meaning they primarily feed on other animals. Their diet consists of a variety of prey that they hunt and consume to meet their nutritional needs. Let’s explore the barracuda’s diet in more detail.
Barracudas are opportunistic hunters, meaning they are not picky eaters and will feed on whatever prey is available to them. Their preferred prey includes small fish, such as anchovies, herring, mullet, and sardines. These fish are often found in schools, making them an attractive target for barracudas.
In addition to fish, barracudas also feed on crustaceans, such as shrimp and crabs, as well as squid and other cephalopods. They have a versatile palate and can adapt their hunting strategies depending on the abundance and availability of different prey species.
To capture their prey, barracudas employ an ambush hunting technique. They patiently wait for the right moment, blending into their surroundings, before launching a sudden and lightning-fast attack. With their impressive speed and powerful jaws, they can swiftly seize their prey and swallow it whole. Barracudas have sharp, needle-like teeth that are designed for gripping and tearing apart their prey, ensuring efficient consumption.
Barracudas are apex predators, meaning they occupy the top of the food chain in their habitats. As such, they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems by controlling the population of smaller fish species.
In terms of nutrition, barracudas obtain essential nutrients, such as protein and fats, from their prey. These nutrients support their growth, reproduction, and overall health. Their carnivorous diet provides them with the energy and resources needed to thrive in their aquatic environment.
It’s important to note that while barracudas are skilled hunters, they are not indiscriminate predators. They have natural instincts and a finely tuned sense of selecting suitable prey based on size, availability, and other factors.
Understanding the barracuda’s diet and nutrition gives us insight into its role as a predator and its contribution to the marine ecosystem. Their carnivorous nature and diverse prey choices demonstrate their adaptability and effectiveness as hunters in the underwater world.
Natural Habitats and Distribution:
Barracuda fish are commonly found in a variety of natural habitats, each contributing to their widespread distribution across different oceans. Let’s explore their natural habitats and where they can be found.
Barracudas inhabit a range of marine environments, including coastal areas, coral reefs, rocky formations, seagrass beds, and open waters. They are well-adapted to both shallow and deeper waters, allowing them to explore a wide range of habitats within their preferred temperature range.
In tropical and subtropical regions, such as the Caribbean Sea, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indo-Pacific region, and the Mediterranean Sea, barracudas are abundant. These warm waters provide favorable conditions for their survival, supporting a diverse array of marine life and serving as their primary habitat.
Coral reefs are particularly attractive to barracudas due to the abundance of prey species that seek shelter and food within the intricate reef structures. The rocky areas and underwater structures also provide hiding places for barracudas to wait for their prey or protect themselves from potential predators.
Seagrass beds are another favored habitat for barracudas. These underwater meadows offer a rich ecosystem with ample food sources and protection for smaller fish, attracting barracudas as they search for their next meal.
Barracudas are known to be highly migratory, moving across different areas within their distribution range. They can be found in various parts of the world, including the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Indian Ocean, the Red Sea, and the Pacific Ocean. Their distribution is influenced by factors such as water temperature, prey availability, and breeding patterns.
It’s important to note that while barracudas have a wide distribution, their abundance may vary within specific regions and their presence may be more prevalent in certain locations than others.
Understanding the natural habitats and distribution of barracuda fish allows us to appreciate their adaptability to different marine environments. Their ability to thrive in various habitats contributes to their ecological significance and their role as top predators in the oceans around the world.
Mating Habits:
Barracuda fish have fascinating mating habits that involve specific behaviors and processes to ensure successful reproduction. Let’s explore the mating habits of barracudas and their unique reproductive journey.
Barracudas engage in a reproductive process known as spawning, where females release their eggs into the water and males release their sperm to fertilize them. This spawning behavior typically occurs in specific seasons or during specific lunar phases, which can vary depending on the species and location.
During the mating season, male barracudas undergo physical changes to attract females. They develop brighter colors, such as increased intensity in their patterns or scales, and may exhibit territorial behaviors to establish their presence and dominance. Males may also engage in courtship displays, such as chasing and circling the female, to demonstrate their readiness to mate.
Once a female barracuda is ready to spawn, she releases her eggs into the water in large quantities. These eggs are tiny and buoyant, allowing them to float freely in the water column. The male barracudas simultaneously release their sperm, which fertilizes the eggs externally.
The fertilized eggs, now developing embryos, drift with the ocean currents. This dispersal strategy increases the chances of survival for the barracuda offspring, as it allows them to explore new habitats and reduces the competition among siblings.
The development of barracuda embryos varies in duration depending on factors such as water temperature and species. It can range from a few days to several weeks. During this period, the embryos undergo growth and transformation, eventually hatching into larvae.
As the larvae emerge, they are vulnerable and rely on the ocean currents to carry them to suitable nursery habitats. Here, they find shelter and ample food sources to support their growth and development.
As the barracuda juveniles grow, they gradually transition into the adult stage, acquiring their characteristic features such as elongated bodies, sharp teeth, and streamlined shapes. The maturation process takes time, and it can vary depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Understanding the mating habits of barracuda fish provides insights into their reproductive strategies and the challenges they face in ensuring the survival of their offspring. The spawning behavior and subsequent development of barracudas highlight their ability to adapt and reproduce in their dynamic marine environments.
Attacks on Humans and Danger:
Barracuda fish are generally not considered a significant threat to humans. While they are powerful predators in their natural habitats, they do not typically pose a danger to humans unless provoked or under certain circumstances. Let’s explore this topic further.
Barracudas are known for their hunting instincts and lightning-fast attacks on prey. However, they do not actively seek out humans as a food source. In most cases, barracudas swim away when encountering humans in the water, preferring to avoid any potential conflict.
While barracudas are generally not aggressive towards humans, there have been reported cases of barracuda-related incidents. These incidents, however, are relatively rare and usually occur when specific conditions align, such as when barracudas are provoked, feel threatened, or mistaken certain reflective objects for prey.
One factor that can contribute to barracuda-related incidents is the presence of shiny or metallic objects, such as jewelry or diving gear, that may resemble the appearance of fish scales. Barracudas, with their predatory instincts, might mistake these objects for potential prey and make sudden lunges. To minimize the risk of such incidents, it is advisable to avoid wearing shiny objects or reflective gear when swimming or diving in barracuda-inhabited waters.
It’s important to note that the majority of encounters between barracudas and humans are peaceful, with barracudas showing no interest in causing harm. They are more likely to swim away or maintain a safe distance when encountering humans in the water.
In any wildlife encounter, it is essential to exercise caution, respect the natural behavior of the animals, and maintain a safe distance. By being aware of the habits and behaviors of barracudas, humans can coexist with these fascinating creatures without unnecessary risks.
Overall, while barracudas are powerful predators, the chances of a barracuda attacking humans are relatively low. Understanding their behavior and taking appropriate precautions can help ensure peaceful coexistence between humans and barracudas in their natural habitats.
Conservation Status:
The conservation status of barracuda fish varies depending on the species and their specific geographical locations. While some populations of barracudas are relatively stable, others face certain conservation concerns. Let’s explore the conservation status of barracudas and the importance of preserving their natural habitats.
Many species of barracuda fish are not currently listed as endangered or critically endangered. However, it is important to note that localized declines or threats to specific populations can occur due to factors such as overfishing, habitat degradation, and pollution.
Overfishing poses a significant threat to barracudas, as they are often targeted by commercial and recreational fisheries. Their popularity as game fish and their value in the seafood market contribute to their exploitation. Unsustainable fishing practices, such as the use of destructive fishing methods or the targeting of large breeding individuals, can have detrimental effects on barracuda populations.
Habitat degradation is another concern for barracudas. Pollution, coastal development, and destructive fishing practices can result in the destruction or alteration of their natural habitats, including coral reefs and seagrass beds. These habitats are essential for their survival, as they provide shelter, food sources, and nursery areas for the young.
Preserving the natural habitats of barracudas is crucial for their long-term survival. Healthy and intact marine ecosystems support the balance of biodiversity and ensure the availability of suitable habitats for barracuda populations to thrive. Conservation efforts focused on the protection and restoration of coral reefs, seagrass beds, and other critical habitats can help safeguard the future of barracudas and the marine ecosystems they inhabit.
Additionally, implementing sustainable fishing practices and regulations is vital in maintaining healthy barracuda populations. This includes enforcing size limits, catch limits, and fishing seasons to prevent overfishing and allow populations to replenish.
Public awareness and education about the ecological importance of barracudas and their habitats are also essential. By understanding the value of these apex predators and the interconnectedness of marine ecosystems, individuals can make informed decisions and actively support conservation initiatives.
In conclusion, while barracudas are not currently listed as globally endangered, localized declines and threats to their populations emphasize the importance of conservation efforts. Protecting their natural habitats, implementing sustainable fishing practices, and raising awareness about their ecological significance are key steps in ensuring the long-term survival of barracudas and the preservation of our marine environments.
Threats and Challenges:
Barracuda fish face several threats and challenges that can impact their populations and overall well-being. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective conservation measures. Let’s explore some of the key threats and challenges faced by barracudas.
1. Overfishing: Barracudas are frequently targeted by commercial and recreational fisheries due to their value as game fish and their popularity in the seafood market. Overfishing can lead to population declines, especially if sustainable fishing practices are not implemented. Removing large breeding individuals can disrupt the reproductive cycle and reduce the ability of populations to recover.
2. Habitat Destruction: Barracudas rely on specific habitats such as coral reefs, rocky formations, and seagrass beds for shelter, foraging, and reproduction. Habitat destruction caused by activities such as coastal development, pollution, and destructive fishing practices can degrade or eliminate these crucial habitats. Loss of habitat reduces the availability of suitable areas for barracudas to thrive and can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems.
3. Pollution: Pollution from various sources, including runoff from land-based activities, industrial discharges, and marine debris, can negatively impact barracudas. Contaminants in the water, such as heavy metals and chemicals, can accumulate in their tissues, affecting their health and reproductive abilities. Pollution can also degrade their habitats and reduce the availability of prey species.
4. Climate Change: The changing climate poses significant challenges to barracudas. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in ocean currents can alter the availability of food sources and disrupt their natural breeding and migration patterns. These changes can impact the overall fitness and survival of barracuda populations.
5. Bycatch: Barracudas can unintentionally end up as bycatch in fishing gear, such as gillnets and longlines, which are primarily targeting other species. Bycatch can result in the incidental capture and mortality of barracudas, adding further pressure to their populations.
Addressing these threats and challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, conservation organizations, and individuals. Implementing sustainable fishing practices, establishing protected marine areas, reducing pollution, and raising awareness about the importance of barracudas and their habitats are vital steps towards their conservation.
By mitigating these threats and promoting responsible stewardship of our marine environments, we can help ensure the long-term survival and ecological balance of barracuda fish and the diverse ecosystems they inhabit.
Edible or Not:
Barracuda fish are consumed in certain regions and have culinary value, but it’s important to note that there are considerations and potential risks associated with their consumption. Let’s explore the topic of whether barracuda fish are safe to eat and the considerations to keep in mind.
Barracudas have been known to harbor high levels of mercury in their tissues, particularly in larger individuals. Mercury is a toxic substance that can accumulate in fish through the food chain. It is important to be cautious when consuming barracuda, especially if caught from certain areas or when consuming large individuals.
Mercury can be harmful to human health, particularly for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and young children. High levels of mercury can negatively affect the developing nervous system and may have other adverse health effects. Therefore, it is recommended to limit the consumption of barracuda, especially for these vulnerable groups.
To ensure the safety of barracuda consumption, it is advisable to follow guidelines and regulations provided by local health authorities and fisheries agencies. These guidelines often include recommendations on consumption frequency, size limits, and areas where barracuda fishing should be avoided.
Additionally, proper preparation and cooking techniques can help reduce the risk of exposure to harmful substances. Removing the skin and fatty portions of the fish can reduce the concentration of contaminants. Cooking methods such as grilling, baking, or broiling can further help in eliminating potential pathogens and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
When considering the consumption of barracuda, it is essential to gather information about the specific species, catch location, and any local advisories or warnings. Staying informed and making informed choices can help ensure the safety of consuming barracuda while minimizing potential risks associated with contaminants.
In conclusion, barracuda fish can be consumed, but there are considerations and potential risks involved. The presence of mercury in their tissues highlights the importance of being cautious, especially for vulnerable groups. It is advisable to follow guidelines and regulations provided by local health authorities and fisheries agencies and to gather information about the specific catch and any local advisories before consuming barracuda. By taking these precautions, one can enjoy barracuda as part of a varied and balanced diet while minimizing potential health risks.
Care:
Keeping barracuda fish in captivity can be challenging and requires careful consideration due to their specific care needs and the potential risks they pose. Let’s explore the care requirements for barracuda fish in captivity and the challenges associated with keeping them as pets.

1. Tank Size and Environment: Barracudas are large, active fish that require spacious tanks with ample swimming space. A tank size of at least several hundred gallons is recommended to accommodate their size and swimming habits. The tank should be well-equipped with hiding spots, rocks, and other structures to mimic their natural habitat. Adequate filtration and regular water maintenance are essential to maintain water quality and prevent the buildup of waste products.

2. Water Quality and Parameters: Barracudas are sensitive to changes in water quality. It is crucial to maintain optimal water conditions, including temperature, pH levels, salinity, and proper oxygenation. Regular monitoring of water parameters and appropriate adjustments are necessary to ensure the well-being of the fish.
3. Feeding: Barracudas are carnivorous predators and require a diet rich in meaty foods. They prefer live or frozen foods such as small fish, shrimp, and squid. Providing a varied and nutritionally balanced diet is important for their health. It is essential to ensure that the food is of appropriate size and quality to prevent choking or nutritional deficiencies.
4. Aggression and Compatibility: Barracudas can be aggressive towards tank mates, especially smaller or slower-moving fish. Careful consideration should be given to tankmate selection to avoid aggressive interactions and potential injuries. Keeping barracudas in a species-specific tank or with large, robust fish that can tolerate their presence is often recommended.
5. Escape Artists: Barracudas are known for their powerful swimming abilities and leaping ability. Special care must be taken to secure the tank with a tight-fitting lid or other means to prevent escape, as they may jump out of the tank if startled or feel threatened.
6. Expertise and Experience: Keeping barracudas as pets requires advanced knowledge and experience in maintaining large, predatory fish. Due to their specific needs and potential risks, it is recommended that only experienced aquarists or professionals with suitable facilities and expertise consider keeping barracudas.
It is essential to note that laws and regulations regarding the ownership and keeping of barracudas vary across different jurisdictions. Before considering keeping a barracuda as a pet, it is important to research and comply with local regulations to ensure legality and responsible ownership.
In conclusion, caring for barracuda fish in captivity requires a significant investment of time, resources, and expertise. Their specific care needs, tank size, water quality, feeding requirements, aggression, and potential risks must be carefully considered. Due to these challenges, barracudas are not commonly kept as pets, and ownership is often restricted to experienced aquarists or professionals.
Legality of Ownership:
The legality of owning barracuda fish as pets varies across different jurisdictions and is subject to specific regulations. It is important to understand and comply with these regulations to ensure responsible ownership and avoid legal issues. Let’s explore the general considerations regarding the legality of owning barracuda fish as pets.
1. Regional Laws and Regulations: Ownership and keeping of barracuda fish are often regulated by regional or national laws. These laws aim to protect native species, prevent the introduction of non-native species, and ensure the welfare of animals in captivity. It is essential to research and familiarize oneself with the specific laws and regulations of the jurisdiction in which you reside.
2. Restricted or Prohibited Species: In some regions, certain species of barracuda or all barracuda species may be restricted or prohibited for private ownership. This is typically done to prevent the introduction of invasive species or to protect threatened or endangered populations. It is crucial to identify the specific species and their legal status before considering ownership.
3. Permit and Licensing Requirements: Depending on the jurisdiction, obtaining permits or licenses may be necessary to legally own and keep barracuda fish as pets. These permits often require individuals to demonstrate their ability to provide appropriate care and facilities for the fish. It may involve inspections, documentation, and adherence to specific guidelines or standards.
4. Trade and Import Restrictions: Barracuda fish may be subject to trade and import restrictions under international agreements such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). These restrictions aim to regulate the international trade of certain species and protect their populations. Compliance with trade and import regulations is essential to ensure the legality of ownership.
It is important to note that regulations can vary widely between countries, states, or even within different municipalities. It is recommended to consult local authorities, such as wildlife agencies, fish and game departments, or environmental agencies, to obtain accurate and up-to-date information on the legality of owning barracuda fish as pets in a specific location.
Failure to comply with legal requirements and regulations can result in penalties, confiscation of the fish, or other legal consequences. Responsible ownership includes understanding and respecting the laws and regulations in place to protect the welfare of animals and the conservation of natural resources.
In conclusion, the legality of owning barracuda fish as pets is subject to regional laws and regulations. It is important to research and comply with the specific regulations of the jurisdiction in which you reside. Identifying restricted or prohibited species, obtaining necessary permits or licenses, and adhering to trade and import restrictions are essential for responsible ownership of barracuda fish as pets. Consulting local authorities can provide accurate information and guidance regarding the legal requirements for owning barracuda fish in a specific location.
Fun Facts:
1. Speed Demons: Barracudas are incredibly fast swimmers, reaching speeds of up to 27 miles per hour (43 kilometers per hour). They zoom through the water with lightning speed!
2. Teeth Galore: Barracudas have a fearsome set of teeth that can be as sharp as needles. Their teeth are designed for capturing and tearing apart their prey. Yikes!
3. Camouflage Masters: Barracudas are expert camouflage artists. They have a unique ability to change their coloration to blend in with their surroundings, helping them hide from both predators and prey.
4. Super Sight: Barracudas have excellent vision. They can spot their prey from a distance and swiftly dart towards it with precision.
5. World Travelers: Barracudas can be found in various warm-water habitats around the world, including tropical oceans and coral reefs. They are true globetrotters!
6. Groupies: Barracudas are known to form schools or groups, especially when they are hunting. These schools can consist of hundreds or even thousands of individuals swimming together. Safety in numbers!
7. Jumping Geniuses: Barracudas are skilled jumpers. They can leap out of the water to catch their prey or escape from predators. It’s like watching an underwater acrobat show!
8. Super Senses: Barracudas have highly developed senses. They can detect vibrations in the water to locate their prey and have a keen sense of smell to sniff out a potential meal.
9. Long-Lived Fish: Some species of barracudas can live up to 15 years or even longer. That’s a lot of swimming and hunting adventures!
10. Size Matters: Barracudas come in different sizes, ranging from smaller species around 1-2 feet (30-60 centimeters) to larger species reaching up to 6 feet (2 meters) in length. That’s one big fish!
Conclusion:
In conclusion, barracuda fish are fascinating creatures that captivate our attention with their unique characteristics and behaviors. Throughout this article, we have explored various aspects of barracudas, shedding light on their scientific name, appearance, habits, diet, and more. Here’s a recap of the key points we’ve covered:
We learned that barracuda fish belong to the Sphyraenidae family, and their scientific name varies depending on the species. They have a streamlined body, sharp teeth, and come in different colors and patterns, such as silver, grayish, yellowish, or black fins.
Barracudas are known for their impressive speed, reaching up to 27 miles per hour (43 kilometers per hour). They can grow to different lengths, from smaller species measuring around 1-2 feet (30-60 centimeters) to the mighty great barracuda reaching up to 6 feet (2 meters) in length.
These fish have diverse habits and lifestyles, preferring warm waters and often forming schools when hunting. They are carnivorous predators with a diet consisting of other fish and small marine creatures.
Barracuda fish are found in various natural habitats, including tropical oceans, coral reefs, and coastal areas around the world. However, they face threats and challenges due to overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change, which emphasize the importance of their conservation.
While barracudas have a fearsome reputation, especially with their sharp teeth, attacks on humans are rare. They generally avoid interactions with humans and focus on hunting their natural prey. Responsible behavior and understanding their habitat can help prevent any potential incidents.
Regarding ownership, the legality of owning barracuda fish as pets varies, and it is crucial to research and comply with regional laws and regulations. Keeping barracudas in captivity requires specialized care and facilities, making them challenging pets to maintain.
In conclusion, barracuda fish are remarkable creatures that contribute to the diversity and balance of marine ecosystems. Their unique physique, hunting prowess, and ability to adapt to different environments make them significant players in the underwater world. Let’s appreciate and protect these magnificent fish to ensure their continued existence for generations to come.
Conclude:
As we conclude our exploration of barracuda fish, let us take a moment to appreciate the wonders of the underwater world. The barracuda’s unique characteristics and the intricate web of life in which it thrives remind us of the diverse and captivating beauty that exists beneath the surface.
By learning about these fascinating creatures, we gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance that sustains our oceans. Let us cherish and respect the rich biodiversity found in marine ecosystems, for they provide us with awe-inspiring sights, valuable resources, and a sense of wonder.
Whether we are snorkeling, diving, or simply observing from afar, let us approach the underwater world with curiosity, appreciation, and a commitment to its preservation. Together, we can ensure that future generations will have the opportunity to witness the breathtaking marvels of nature beneath the waves.
So, next time you find yourself near the ocean or exploring an aquarium, take a moment to reflect on the barracuda fish and the countless other species that call the depths their home. Through our understanding and responsible actions, we can protect and preserve these remarkable creatures and their habitats for generations to come.
Let us continue to explore, learn, and be stewards of the precious marine world, for it holds an abundance of beauty, mystery, and inspiration that is truly worth protecting.

